实现一个 Vue-Router
1. 实现原理
hash 和 history都是实现前端路由的浏览器历史记录API。相对而言 history 比 hash 更为强大。
1.1 Hash
| 属性 & 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
window.location.hash = '' |
向历史记录中压入一个新记录,window.location.hash值发生变化后,会在浏览器添加一条新记录 |
window.location.replace() |
用给定的URL替换调当前的资源,被替换的页面不会被保存在会话的历史中。 |
window.hashchange事件 |
在浏览器URL中hash发生变化后触发。URL中#后的内容就是hash,hash变化不会向服务器发起请求。 |
2.2 History
History API允许操作曾经在浏览器标签页访问的会话历史记录。
| 属性 & 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
history.length |
当前历史记录栈的个数 |
history.back() |
前往上一页,点击浏览器返回按钮可模拟此方法,等价于history.go(-1) |
history.forward() |
前往下一页,点击浏览器前进按钮可模拟此方法,等价于history.go(1) |
history.go() |
通过当前页面的相对位置,跳转到某个历史记录页面 |
history.pushState(stateObject, title, url) |
向浏览器的历史堆栈压入一个新记录,并改变历史堆栈的当前指针至栈顶。stateObject: 用于存储该url对应的状态对象,该对象可在onpopstate事件中获取,也可在history对象中获取;title: 标题,目前浏览器未实现; url: 一般设置为相对路径,如果设置为绝对路径时需要保证同源。 |
history.replaceState() |
这个接口和pushState参数相同,区别在于replaceState是替换浏览器历史堆栈的当前历史记录。需要注意的是,replaceState不会改动浏览器历史堆栈的当前指针。 |
window.onpopstate事件 |
历史堆栈的当前指针改变,则会触发onpopstate事件 |
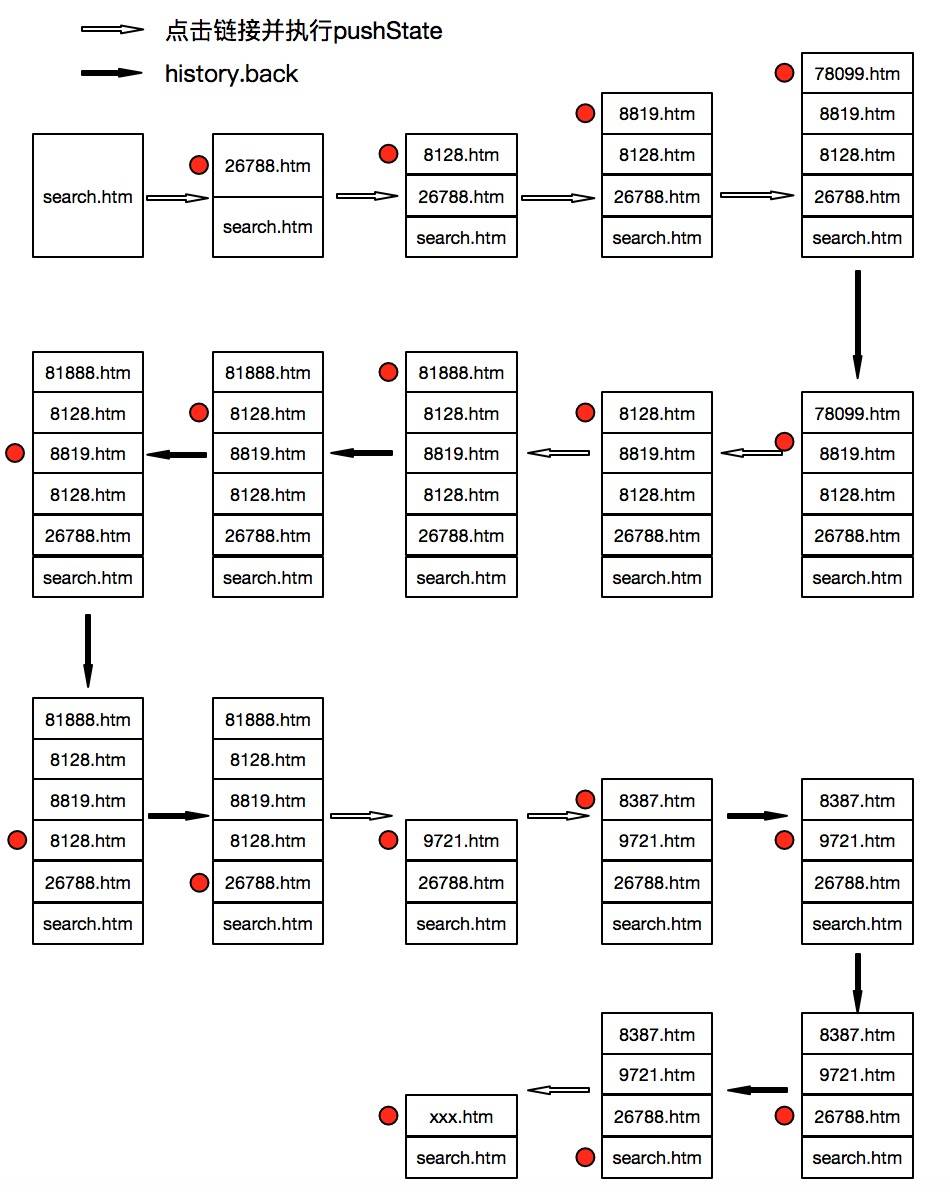
点击浏览器的前进、后退按钮,执行history.forward, history.back和history.go都会修改历史堆栈的当前指针。在不改变document的前提下,一旦当前指针改变则会触发onpopstate事件。
浏览器没有提供访问页面的历史记录栈的接口,但是它提供了history.length属性,它表明了当前历史记录栈的个数。它可以帮我们分析history API对历史记录栈的影响。
下图说明了:
- 执行
window.history.go,history.back,history.forward时,history栈大小不会改变,仅仅移动当前指针的位置 - 执行
pushState时,会在当前指针上压入一个url入栈顶,同时修改当前指针
2. 实现功能
Vue Router功能:
- Router构建选项
mode: 支持HTML5 History, hash, abstract模式 - Router构建选项
routes: 支持传入{ path: string, component: Component } - 使用
<router-link>来定义导航链接 - 使用
<router-view>渲染路径匹配到的视图组件 - 使用
this.$router.push(),this.$router.replace,this.$router.go实现路由跳转 - 使用
this.$route.params,this.$route.query获取路径参数 实现Router的生命周期钩子(执行顺序)
动态路由匹配
- 嵌套路由
- 嵌套视图
- 导航守卫
- 过渡动效
- 路由懒加载
3. 开始实现
1 | const router = new VueRouter({ |
3.1 创建VueRouter实例
创建一个Vue Router实例,接收mode, routes参数
- 为
this.$router提供路由push,replace,go,back,forward方法 - 将传入的routes转成routerMap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51// src/index.js
import HashHistory from '../history/hash'
import HTML5History from '../history/html5'
import AbstractHistory from '../history/abstract'
import { createMatcher } from './create-matcher'
export default class VueRouter {
constructor(options) {
this.app = null
this.apps = []
this.options = options
this.mode = options.mode || 'hash'
this.fallback = options.mode === 'history'
this.history = null
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this) // 路由匹配对象
switch(this.mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this)
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this)
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this)
break
default:
console.log(`invalid mode: ${this.mode}`)
}
}
push(location) {
this.history.push(location)
}
replace(location) {
this.history.replace(location)
}
go(n) {
this.history.go(n)
}
back() {
this.go(-1)
}
forward() {
this.go(1)
}
}
3.3 router, route
Vue.use(Router)时,会执行install方法并把Vue类传入,混入beforeCreate方法- 将
$router,$route放到Vue.prototype上,保证每个Vue实例都可以访问 - 定义全局组件
router-link,router-view1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46// install.js
import View from '../components/view'
import Link from '../components/link'
export default function install(Vue) {
const isDef = v => v !== undefined
// 应用里的每个Vue实例都会执行这个函数
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// 判断是否是根组件,只有根组件上有router对象
if (isDef(this.$options.router)) {
// 根组件路由
this._routerRoot = this
this._router = this.$options.router
this._router.init(this)
// 为_route属性实现双向绑定,触发组件渲染
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current)
} else {
// 子组件路由
this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this
}
},
})
// 设置全局访问变量
// _routerRoot 指向Vue实例
// _router 指向VueRouter实例
// $router 当前Router实例
// $route 当前Route信息
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', {
get() { return this._routerRoot._router }
})
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', {
get() { return this._routerRoot._route }
})
// 定义全局组件router-link, router-view
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link)
Vue.component('RouterView', View)
const strats = Vue.config.optionMergeStrategies
strats.beforeRouteEnter = strats.beforeRouteLeave = strats.beforeRouteUpdate = strats.created
}
3.4 HTML5 History模式
还有hash模式、1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44import { START } from '../util/route'
export default class HTML5History{
constructor(router) {
this.router = router
this.current = START
window.addEventListener('popstate', e => {
this.transitionTo(this.getCurrentLocation())
})
}
// 修改this.current值
transitionTo (location) {
// 修改current的值
const route = this.router.match(location, this.current)
this.current = route
// 修改所有app下的_route值,触发RouterView重新渲染
this.cb && this.cb(route)
}
getCurrentLocation() {
let path = decodeURI(window.location.pathname)
return (path || '/') + window.location.search + window.location.hash
}
push(location) {
// pushstate
this.transitionTo(location)
window.history.pushState(null, '', location.path)
}
replace(location) {
// replacesstate
this.transitionTo(location)
const stateCopy = Object.assign({}, history.state)
window.history.replaceState(stateCopy, '', location.path)
}
go(n) {
window.history.go(n)
}
}
3.8 Router-View组件
1 | export default { |
3.9 Router-Link组件
1 | export default { |
4. 钩子函数
4.1 全局守卫
router.beforeEach(to, from, next)进入路由前router.beforeResolve(to, from, next)router.afterEach(to, from)1
2
3
4
5const router = new VueRouter({ ... })
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
})
4.2 路由独享守卫
beforeRouteEnter进入路由前beforeRouteUpdate路由复用同一个组件时beforeRouteLeave离开路由时1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
// 不能获取组件实例 `this`,组件实例还没被创建
},
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用 可以访问组件实例 `this`
// 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id,在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候,
// 由于会渲染同样的 Foo 组件,因此组件实例会被复用。而这个钩子就会在这个情况下被调用。
},
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
// 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用,可以访问组件实例 `this`
}
}
]
})
4.3 组件级守卫
参数或查询的改变并不会触发进入/离开的导航守卫。你
